.Home|Veiw Shopping Cart|Privacy Policy|Contact Us

Clinical Studies Prove That RESPeRATE Works
We at AlkalizingNutrition.com are of a non-drug mentality. It is our firm belief that humans are not deficient in drugs. We are fearfully and wonderfully made, and our bodies can heal itself when given the ingredients our Heavenly Father naturally provides. That being said, we respect the scientific due diligence put into RESPeRATE. Being aware of the skepticism of the medical community to anything non-medical, several scientific tests were conducted to prove RESPeRATE'S ability to reduce blood pressure. Because of these rigorous tests no one can question the efficacy of RESPeRATE to effectively lower blood pressure and reducing the negative effect of this silent killer.
Scientific Rigor
Well-controlled clinical trials before and after FDA approval have validated RESPeRATE's blood pressure lowering claim. Anticipating initial skepticism regarding the efficacy of device-guided paced breathing, special attention was given to study design and understanding of the physiological mechanisms.
Study Design & Population
- The studies compared those who used RESPeRATE for 15 minutes a day for 8 weeks to a "control" group, using a walkman with relaxing music1, a home blood pressure monitoring 4,5 or both 2
- Clinical studies design included four double-blind and randomized1,2,5,8, one controlled and randomized4, and two open-label studies3,6
- There were 286 participants, average age of 58
- 78% of participants were already taking blood pressure medications, a third of whom were taking more then 3 medications.
- Average initial office blood pressure of 150/90 mmHg despite using diet, exercise and/or medications.
Results
RESPeRATE users with uncontrolled blood pressure experienced a significant decrease in office blood pressure by up to 36 points systolic and 20 points diastolic (top 10% reductions) with average reduction of 14/8 mmHg points.
Control treatment reduction was 9/4 mmHg, significantly less than with RESPeRATE (p = 0.008 and p = 0.002, respectively for systolic and diastolic blood pressures).
The results were similar across genders and medication status.
The drop in office BP was directly related to the duration of slow
breathing; those who used RESPeRATE more achieved better reductions.
A sustained reduction in blood pressure typically occurred in 3 to 5 weeks.
Larger reductions in office blood pressure occurred in older individuals and those with higher baseline blood pressures, whether taking antihypertensive medication or not.
Home blood pressure measurements (for up to 6 months of use7) and 24-hours ambulatory blood pressure monitoring5 have verified an all-day, lasting blood pressure lowering effect.
Patients' ability to operate the RESPeRATE device without prior training and to comply with routine use were established objectively using the device's internal memory and verified by post-market surveys.
RESPeRATE Reduces Severity of Hypertension
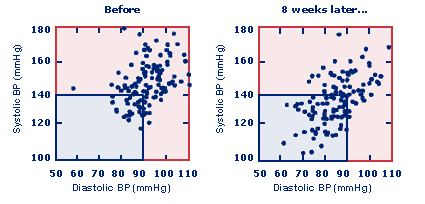
The chart below are stunning proof from a study of 141 patients showing RESPeRATE's ability to naturally reduce high blood pressure without drugs and their side effects.
Each point represents the office systolic BP of the 141 patients in the RESPeRATE treatment group. Notice that after 8 weeks more of the patients systolic BP was lowered into the (blue area) 140/90 range.
These are real results from real people represented by each of these dots. If you are concerned a loved one, your mom, your dad, your wife, or your husband, and you want to reduce the occurrence of an unwelcome surprise shouldn't you be telling that loved one about this ingenious device? Remember just having health insurance in no assurance of good health. We must take responsibility and do whatever we can to prevent catastrophic illness. An once of prevention is worth more than a pound of cure.
References
[1] Schein M, Gavish B, Herz M et al. J Human Hyperten 2001; 15(4): 271 - 278. > [2] Meles E, Giannattassio MF, Gentile G, Capra A, Mancia G. Am J Hyperen 2004, 17:370-374. [3] Elliott W, Izzo J, White W, Rosing D, Snyder C, White W, Alter A, Gavish B, and Black B J Clin Hyperten 2004; 6(10)553-559. [4] Grossman E, Grossman A, Schein MH, Zimlichman R, Gavish B J Human Hyperten 2001; 15(4): 263 - 269. [5] Rosenthal T, Alter A, Peleg E, Gavish B. Am J Hyperten 2001; 14(1): 74 - 76. [6] Viskoper R, Shapira I, Priluck R, Mindlin R, Chornia L, Laszt A, Dicker D, Gavish B, Alter A. Am J Hyperten; 2003; 16:484-487. [7] Meles E, Giannattasio G, Boff L et al. Italian Society of Hypetension National Meeting, Bologna Italy, September 2002. [8] Schein MH, Alter A, and Gavish B. J Clin Hyperten, 2006, Vol 8, Issue 5, Supl A,. P- 79. [9] Bae JH, Kim JH, Choe KH, Hong SP, Kim KS, Kim CH and Kim WH. J Clin Hyperten, 2006, Vol 8, Issue 5, Suppl A,. P-86, [10] Kim JY, Han MS, Yoo HH, Choe HM, Yoo BS, Lee SH, Yoon J, and Choe KH. J Clin Hyperten, 2006, Vol 8, Issue 5, Suppl A. [11] Parati G, Glavina F, Ongaro G, Maronati A, Gavish B, Castiglioni P, Di Rienzo M, Mancia G. Amer J Hyperten 2002; 15(4,2)182A [12] Asanoi H, Goso Y, Yamazaki T, et al. Circulation Journal 2004, 68 (Suppl I), 184. [13] Parati G, JL Izzo Jr, B Gavish, in Hypertension Primer, Third Edition. JL Izzo and HR Black, Eds. Baltimore, Lippincott, Williams, and Wilkins, 2003; Ch. A40, p117-120. [14] Kim JY, Han MS, Yoo HH, CHoe HM Yoo BS, Lee SH, Yoon JH, Choe KH. J Clin Hyperten, 2006, Vol 8, Issue 5, Suppl A. A212
Home|Privacy Policy|Contact Us|Return Policy|Disclaimer
Copyright © 2007. AlkalizingNutrition.com, Inc. All rights reserved.